D&R Insights: How is the ASI Performance Standard driving action on gender equity
The ASI Performance Standard V3 addresses gender equity and women’s empowerment directly under Criterion 9.2. The criterion requires all Entities to implement programs that address gender gaps across various aspects, such as employment practices, training opportunities, awarding of contracts, processes of engagement, management activities.
27 March 2024
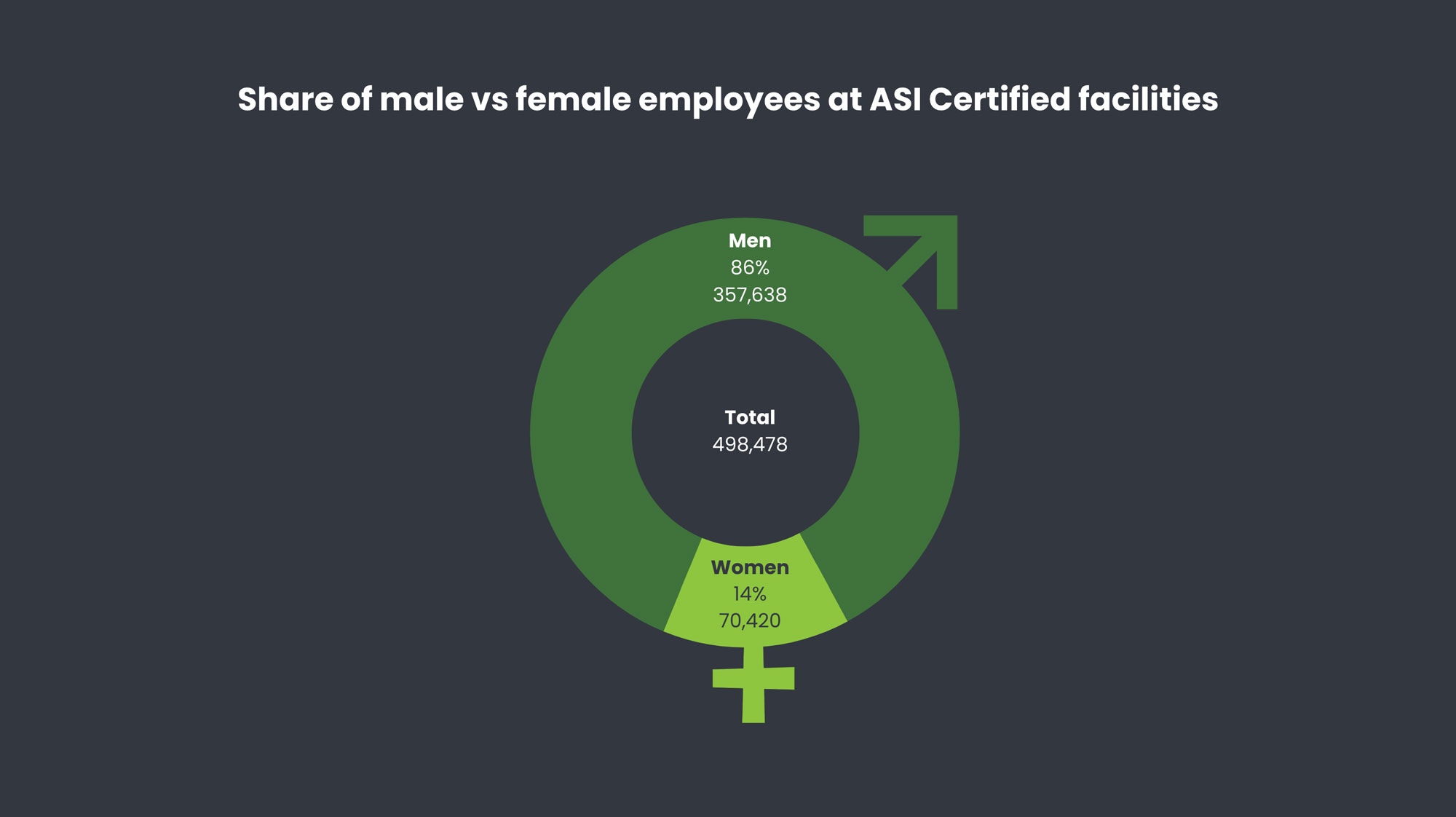
Data from 233 current ASI Performance Standard (PS) Certifications (as of 31/12/2023), show that just over 70,000 women are working in ASI PS Certified facilities globally, constituting 14 percent of the total workforce at these facilities.
Gender Equity and Women’s Empowerment under ASI Performance Standard V3
ASI Performance Standard V3 addresses gender equity and women’s empowerment directly under Criterion 9.2. The criterion requires all Entities to implement programs that address gender gaps across various aspects, such as employment practices, training opportunities, awarding of contracts, processes of engagement, management activities.
However, the emphasis on women’s rights is not confined to a single criterion but is integrated across the Performance Standard:
- differential impacts on women should be identified in the Human Rights Impacts Assessment (criterion 2.6) as part of a gender-responsive Policy commitment and mitigation under Human Rights Due Diligence (criterion 9.1),
- women from Indigenous Peoples groups should be fairly represented during consultations with Entities (criterion 9.3 Indigenous Peoples, criterion 9.4 Free Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC), criterion 9.7 Affected Populations and Organisations),
- gender-sensitive mechanisms are crucial when addressing displacement and developing livelihood restoration plans, with special attention to women’s unique community roles (criterion 9.6 Displacement),
- for rights violation, ensure women face no barrier in Complaints Resolution Mechanism (criterion 3.4 Stakeholder Complaints, Grievances and Requests for Information).
What notable actions are being undertaken by ASI-Certified Entities?
ASI-Certified Entities are actively pursuing initiatives to respect women’s rights and interests and increase participation of women in the workforce through the adoption of inclusive policies and practices. Practical examples from the ASI-Certified cohort include:
- targets for increased participation of women,
- creating a forum supporting women’s professional development and career advancements,
- active promotion of female roles in engineering at local schools,
- support to local associations focused on addressing women’s issues, and
- participation in the Bloomberg Gender Reporting Framework and national gender pay gap disclosure initiatives.
It is important to regularly review policies and practices towards improving gender equity aspects of, for example, recruitment and selection panels, educational opportunities, promotions and career advancement, remuneration and pay gap, protection of health and related benefits, and situation-based working arrangements.
These and other actions can “inspire inclusion” and help drive towards a greater representation of women in the aluminium sector workforce.
“Gender equality is not only a fundamental Human Right, but a necessary foundation for a peaceful, prosperous and sustainable world.”
The UN Sustainable Development Goals recognise the importance of women’s empowerment – but the world is not on track to achieve gender equality by 2030. By implementing inclusive policies and practices, ASI Entities and individuals – whether as part of an organization, or as a leader in the aluminium value chain — can make important contributions.
Additional information
- Developing a program that promotes gender equity and women’s empowerment can be found at the UN Global Compact: Women’s Empowerment Principles.
- Measuring the impact of gender equity and women’s empowerment programs can be found in the BSR Making Women Count Report and Toolkit.
- ASI has developed a specific course for ASI auditors on ‘Adopting a gender-sensitive approach to auditing’, available on educationAL.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE


