Embracing Circularity: Building a Sustainable Aluminium Value Chain with ASI
The Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) is committed to fostering an aluminium value chain that is both circular and resource-efficient, and has thus established Circularity as one of its four sustainability priorities, as well as one of its long-term strategic goals.
12 July 2023
The Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) is committed to fostering an aluminium value chain that is both circular and resource-efficient, and has thus established Circularity as one of its four sustainability priorities, as well as one of its long-term strategic goals. To this end, ASI continues to develop and promote criteria and guidance regarding Material Stewardship within its Performance Standard and Chain of Custody Standard, and is committed to encouraging the adoption of circular economy principles within the industry.
Sustainability is not a solo endeavour, but a shared responsibility. Every entity in the aluminium value chain, from bauxite mining to aluminium recycling, plays a crucial role in the shift towards a circular economy. This collective action propels us towards a future where materials are used efficiently and circulated endlessly, resulting in environmental, economic, and societal benefits. The key benefits of a transition to a circular aluminium value chain include:
- reduced environmental impact: A circular aluminium value chain can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and waste, while conserving finite resources.
- creation of new jobs and opportunities, and boosted economic resilience. It can provide opportunities for businesses to develop new products and services while reducing the cost of raw materials.
- improvements to public health and well-being, and support for a more just and equitable society.
ASI is actively contributing to this transition, working alongside other organizations that define and implement circularity in various ways. Its primary objective is to foster a culture of inclusivity and knowledge sharing, ensuring that all stakeholders feel engaged and equipped for this transformative journey. ASI strives to provide practical examples and develop comprehensive indicators that measure circularity at an entity level, offering clear and accessible pathways for all industry participants to collectively work towards a truly circular and sustainable aluminium sector.
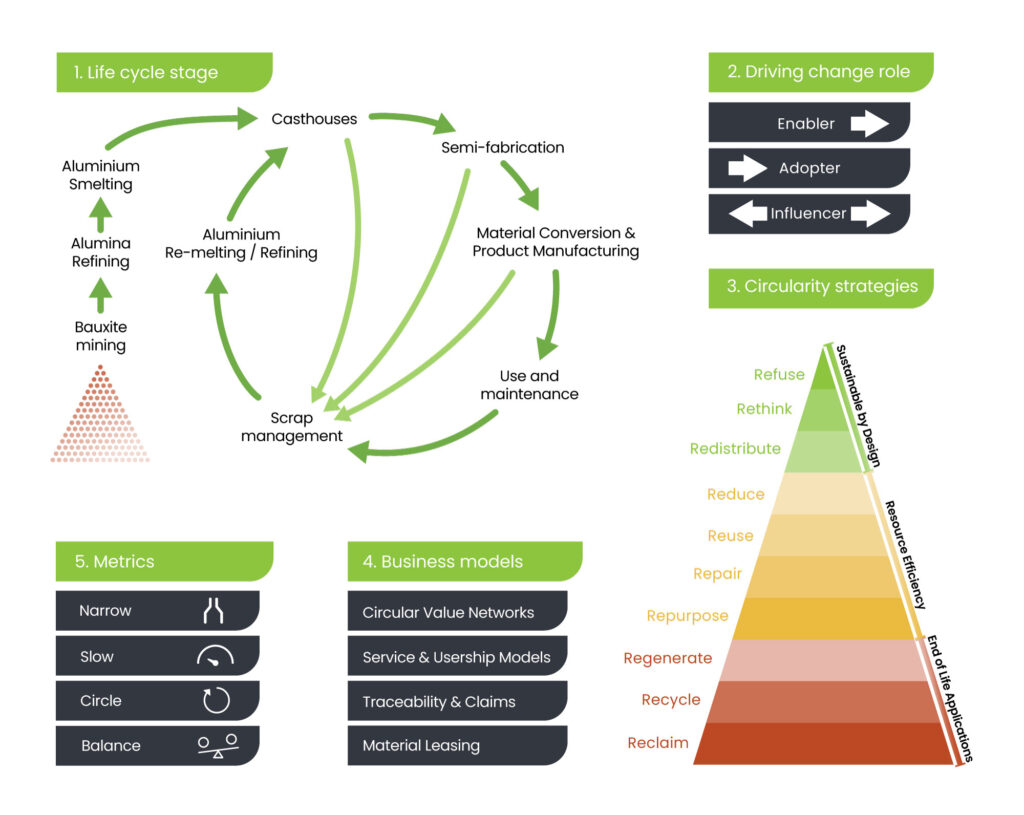
ASI Circularity Framework: A visual representation of ASI's integrated framework for achieving circularity in the aluminium value chain. Note: This graphic illustrates the key elements of 1) the lifecycle stage, 2) driving change role, 3) circularity strategies (10 Rs), 4) circular business models, and 5) metrics. It communicates the approach for achieving a sustainable circular aluminium value chain.
The transition to a circular aluminium value chain is not without challenges. Technical obstacles, such as the need to enhance post-consumer collection methods, the requirement for efficient sorting techniques, and the need to improve the quality of scrap aluminium are coupled with economic hurdles, such as significant upfront investments, which have impeded progress. Working Groups within ASI facilitate discussions to address these issues, and the momentum towards a circular aluminium value chain is steadily growing, driven by recognition of its manifold benefits.
The transition towards a circular economy necessitates the adoption of innovative business models. The aluminium industry is well-positioned to adopt a circular economy due to the unique properties of the material. Recycling is a crucial part, but there are many other strategies and practices to reduce waste and keep aluminium in circulation, such as designing products for durability and easy disassembly. Within the aluminium value chain, businesses are exploring value networks, service-based models, and improved traceability to encourage circular practices. For example, material leasing allows for the utilisation of aluminium as a service, reducing waste and fostering resource efficiency. By shifting from a traditional ownership model to a usership model, businesses can maximise the value derived from aluminium whilst minimising environmental impacts.
ASI’s aspiration to foster enhanced circularity in the aluminium value chain through both of its Standards, collaboration with stakeholders, and leadership on collective action serves as a potential guide for other industries. These activities aim to demonstrate circularity’s potential to mitigate environmental impacts, optimise resource use, and enhance the sustainability of the entire aluminium value chain. The future of the aluminium industry is circular, and we invite interested stakeholders to engage with us on this journey.
More information on ASI’s circularity work
- Watch the recent webinar: 45 Minutes on… Circularity Assessment: Enhancing Efficiency in the Circular Economy
- Consult the Circularity sustainability priority web page
RELATED TOPICS:
SHARE THIS ARTICLE


